Human Capital Rating System Available at No Cost
JP Morgan Chase Has Much Room for Improvement, Ratings Find
A process for rating the organizational maturity of organizations developed in the United Kingdom is now available at no cost to help organizations “develop a greater understanding and the professional practice of organization maturity and human governance,” according to statement by Maturity Institute (MI) and Organizational Maturity Services (OMS) LLP. Organizations can use the methodology to score themselves, their clients, or companies in which they are considering an investment. See previous ESM article on the Maturity Institute and its OMINDEX.
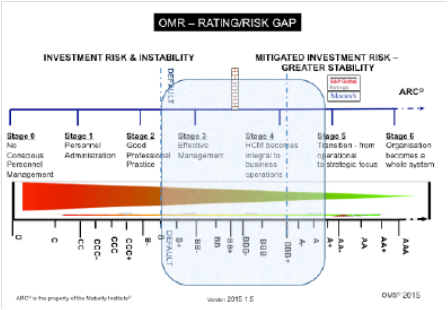
The Maturity Institute recently used the template to rate JP Morgan Chase. Based on a review of filings and public ratings, JP Morgan received a B grade, with much room for improving shareholder value, lowering risks and creating a more engaging work environment. See below for more details.
 According to Stuart Woollard, Partner, OMS LLP, “Sharing this methodology will show boards, investors and key stakeholders the power of Organizational Maturity to analyse and measure so- called intangibles such as corporate culture, human governance and workforce management and, at the same time, understand their impact on sustainable value and material business risk. We know from our own experience with companies and the investment community that this is compelling technology that enables comparative measures of critical organizational factors that are currently missing. It also facilitates the design of roadmaps for powerful organizational change to make companies fit for purpose in today’s evolving business paradigm.”
According to Stuart Woollard, Partner, OMS LLP, “Sharing this methodology will show boards, investors and key stakeholders the power of Organizational Maturity to analyse and measure so- called intangibles such as corporate culture, human governance and workforce management and, at the same time, understand their impact on sustainable value and material business risk. We know from our own experience with companies and the investment community that this is compelling technology that enables comparative measures of critical organizational factors that are currently missing. It also facilitates the design of roadmaps for powerful organizational change to make companies fit for purpose in today’s evolving business paradigm.”
Adds Paul Kearns, MI Chair: “We also see this as a crucial step in helping OM30+© become the defining global standard for measuring comparative organizational maturity which is linked to sustained value creation and risk mitigation. The original design of OMINDEX is aimed for ratings to sit alongside traditional credit ratings, which are unable to provide good whole system insight into current and future corporate ‘health’. We have now begun to see this aim being realized and hope sharing this IP (Intellectual Property) will greatly move us forward.”
The Maturity Index rating process was recently used by the Maturity Institute to rate Chase Bank, which received a grade of B, with a Total Stake Holder Value of 0.53 and a risk factor of 63%. Woollard says this means that Chase could nearly double its stakeholder value with a more strategic focus on human capital and significantly reduce risks to stakeholders. For instance, he noted, JP Morgan Chase has paid more than $28 billion in fines and penalties – funds that could be more productively deployed.
The ratings were based in part on the following conclusions from publicly available filings and information sources:
- There is a significant gap between the organization’s public statements and external communications and the reality found in the evidence. This leads us to question the authenticity of JP Morgan’s declared principles and practices.
- CEO remuneration has moved away from JP Morgan’s founding principle of an equitable reward system linking CEO pay to the workforce. It is now financially geared, encourages a focus on short-term earnings and, when set against MI’s global standard of TSV (Total Stakeholder Value), the CEO’s contribution falls short.
- JP Morgan’s statement of purpose: “First class business... in a first class way” is contradicted by strong evidence of business conduct that continues to cause reputational damage.
- JP Morgan’s Board has a conventional committee structure with shareholder interests being its prime concern.
- JP Morgan’s post-GFC strategy of a “Fortress Balance Sheet” and “Fortress Controls” reads across to the creation of an unhealthy “Fortress Culture” that is largely impervious to external critique.
- Performance management and executive reward is rooted in driving shareholder returns. In particular, the “People & Leadership” dimension is not connected to material value or risk outcomes. For example, JP Morgan claims success (Proxy Statement, 7 April 2016) is simply having “Created a new leadership development program...”
- Customer/client service is seen as fundamental to JP Morgan’s definition of business success (i.e., to provide shareholder value). Some improvement is evident, but it still lags behind the best in class. The litany of misconduct suggests that it strategic emphasis on quality is overplayed and under-delivered. We also see this as an indication of an unhealthy disregard for the regulatory environment.
- JP Morgan’s instances of misconduct include a recent “bribery” issue in China, a whistle blower sacking and “mortgage abuses.” The bank is either wholly unaware of, or in denial about, the extent to which this is symptomatic of its culture, simply stating in its 2015 Annual Report: “the conduct of a small group of employees, or of even a single employee, can reflect badly on all of us and can have significant ramifications for the entire firm.” This statement fails to identify what, if any, remedial management actions are required.
- Culture and conduct initiatives have largely been a standard ‘boiler plate’ strategy e.g. issuing and promoting business principles and widespread training thereon. The company’s Chief Operating Officer has responsibility for culture and conduct program, and not human resources, but capability needs building here.
- Management practice deploys conventional human resources processes focusing on talent attraction and retention, with a significant emphasis on diversity programs. This does not meet the MI standards of mature human capital management.
- Innovation is primarily centred on technology investments to drive efficiencies, customer interaction and cross-selling. There is no strong evidence that an underlying, ‘human’ led, firm-wide system of knowledge capture, sharing and value creation is in place.
The Maturity Institute (MI) comprises a global network of professionally accredited leaders, practitioners and academics creating value for all stakeholders through organizational maturity that realises the full value of human potential for the benefit of society.
For More Information
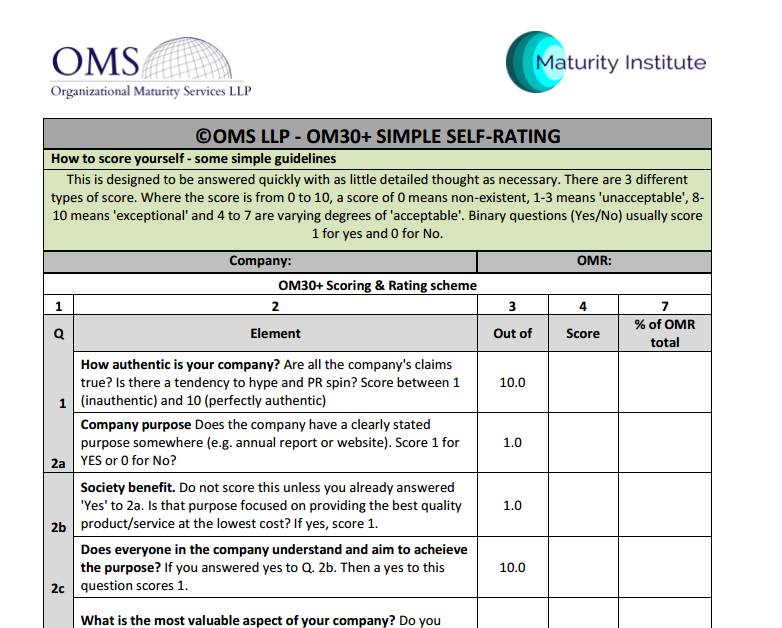
To obtain a copy of the OM30+ spreadsheet for self-scoring your organization, send your details (Name, Organization, Job Title) to Stuart Woollard. An outline pdf copy of the OM30+ is available online. The full working template is available here.














